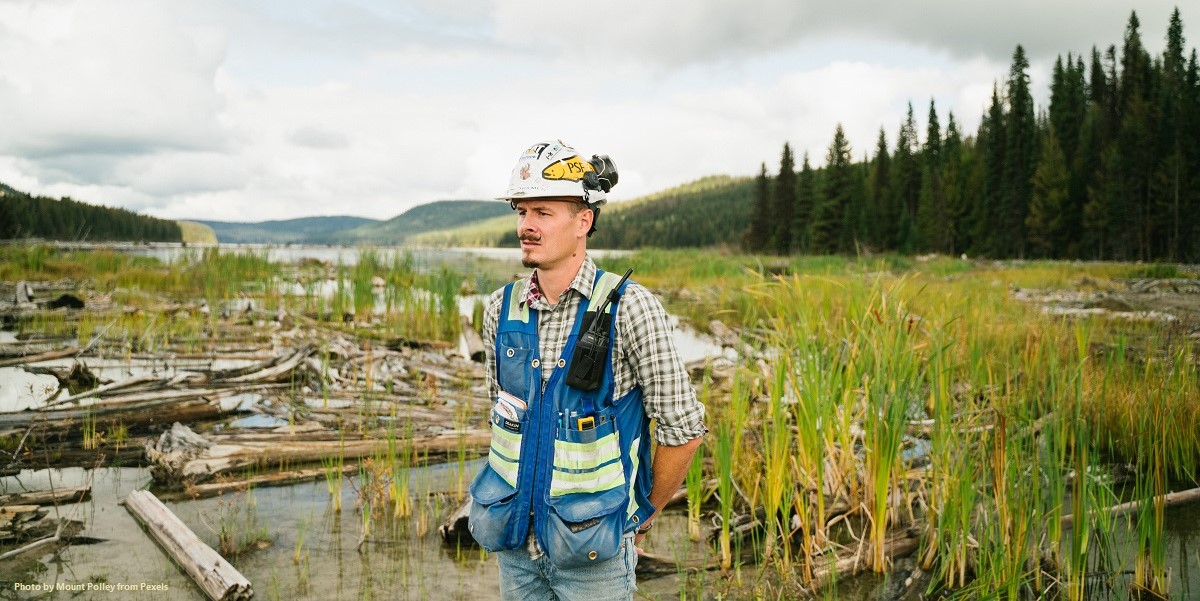
Environmental engineering is a branch of applied science and technology that is designed to address the issues of energy preservation, protection of assets, and control of waste from human and animal activities, including managing public health solutions.
Environmental engineering is concerned with the measurement, modelling, control, and simulation of all types of environments. It is an interdisciplinary subject, bringing together aspects of mechanical, an electrical, electronic, aeronautical, civil, energy, and chemical engineering.
Environmental engineers develop solutions to waterborne diseases and push for the implementation of laws promoting adequate sanitation in urban, rural, and recreational areas. They also focus on waste-water management, air pollution control, recycling, waste disposal, radiation protection, industrial hygiene, animal agriculture, environmental sustainability, and public health.
Although environmental engineers have many responsibilities to manage, one of the most important responsibilities is to prevent harmful chemicals and biological contaminants to be released into the air, water, and soil. To prevent such mishaps, environmental engineers must have an extensive knowledge of the chemistry and biology of the potential contaminants as well what industrial or agricultural processes might lead to the release of these chemicals. By knowing this, new processes can be designed, and existing processes can be modified, to reduce or eliminate the release of pollutants.
Another important function performed by environmental engineers is determining the source of pollutants. Sometimes this can prove to be a difficult task given the expansive terrain that drains to bodies of water. Once the contamination is discovered, it must be stopped or significantly reduced. Environmental engineers often work with businesses to provide ways to avoid or reduce the production of pollutants. If impossible to sufficiently reduce the output of pollutants, they engineer ways to separate and dispose of the contaminants safely. They design systems, processes, and equipment to restore air, soil, and water quality.
To do all this effectively, environmental engineers must possess a working knowledge of chemical engineering, fluid dynamics, geography, geology, and hydrology, as well as applicable laws that impact their work.
21st Century Skills required for this profession:
Critical Thinking
- Determine sources of pollutants using a wide range of data
- Analyze multi-faceted scenarios
- Evaluate chemical compounds
Collaboration
- Coordinate with groups on skillsets and techniques for remediation
- Establish and communicate project timelines
Communication
- Clearly communicate analyses
- Provide oral and written reports to explain the issues and proposed solutions
Creativity
- Develop new ways to prevent and remedy environmental disasters that impact public health
MyStemKits is a collection of standards-driven lessons that can be used with hardware such as 3D printers, robotics systems, and sensors. A few MyStemKits kits that could spark interest in environmental engineering include the City Engineering Kit, Water Filtration Kit, and Planetary Temperatures Kit. To see how the Planetary Temperatures Kit works, watch the video:
Boxlight MimioSTEM solutions offer a variety of materials that every educator can use to support STEM learning. To learn more about MimioSTEM solutions, go to boxlight.com/stem-education.